Table of Contents
Introduction to Digestive Health
Our digestive health is a cornerstone of overall wellness, though it often goes unnoticed until problems arise. The digestive system, including organs like the stomach, intestines, and liver, is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing vital nutrients, and eliminating waste. This complex process ensures our bodies receive the energy and nutrients needed for daily functioning.
Beyond nutrient absorption, a well-functioning digestive system is crucial for a strong immune system, efficient metabolism, and even mental health. The gut hosts trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome, which play a significant role in both physical and mental well-being. These microorganisms assist with digestion, produce essential vitamins, and protect against harmful pathogens.
Digestive health issues are common, affecting millions of people worldwide. Conditions like indigestion, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and more severe disorders such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are prevalent. Poor diet, stress, lack of exercise, and certain medications can all contribute to these problems. The key to preventing and managing these issues lies in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
Incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into your diet can greatly enhance gut health. Probiotics, often called “good” bacteria, introduce beneficial microorganisms to the gut. Prebiotics, on the other hand, act as food for these microorganisms, encouraging their growth and activity. Together, they create a synergistic effect that can significantly improve digestive health.
Understanding the basics of digestive health and the critical role of the gut microbiome sets the stage for exploring how probiotics and prebiotics can be leveraged to naturally improve your digestive well-being.
Understanding Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms, often dubbed “friendly” or “good” bacteria, that offer substantial health benefits when consumed in appropriate amounts. They primarily reside in the gastrointestinal tract and are vital for maintaining a balanced gut microbiota, which is essential for optimal digestive health. Probiotics come in various types, each with different strains that provide unique benefits.
The most recognized probiotic strains include Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Lactobacillus strains are known for producing lactic acid, which lowers the pH of the intestines, making it harder for harmful bacteria to thrive. Bifidobacterium strains, on the other hand, help digest dietary fiber and prevent gastrointestinal infections.
Each probiotic strain has its own specific benefits. For instance, Lactobacillus acidophilus aids in lactose digestion and can help alleviate symptoms of lactose intolerance. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG is effective in reducing the duration and severity of diarrhea. Bifidobacterium bifidum supports immune function and strengthens the gut barrier, helping to prevent the invasion of pathogens.
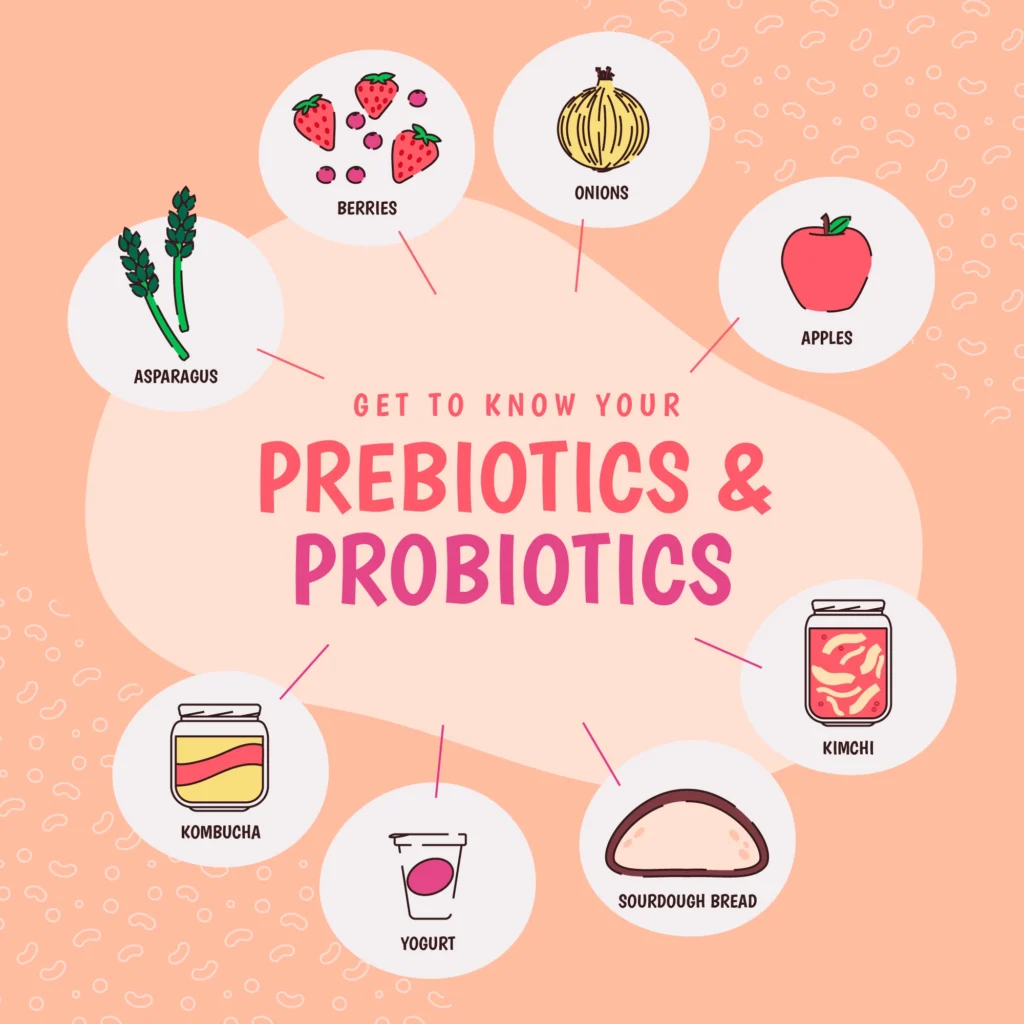
Natural sources of probiotics include fermented foods and beverages that have been consumed for centuries in various cultures. Foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso are rich in probiotics. These foods not only provide the live bacteria needed for gut health but also contain other nutrients that benefit overall wellness. For those who may not consume enough fermented foods, probiotic supplements are available. These supplements come in various forms, such as capsules, powders, and liquids, making it easy to incorporate the best probiotic for gut health into your daily routine.
By regularly including probiotics in your diet through food or supplements, you can enhance your digestive health, improve nutrient absorption, and strengthen your immune system, ultimately contributing to better overall health.
Understanding Prebiotics
Prebiotics are specialized plant fibers that nourish the beneficial probiotic bacteria in our intestines. Unlike probiotics, which are live microorganisms that directly introduce beneficial strains into the digestive system, prebiotics act as a food source for the existing beneficial bacteria. This essential difference highlights the importance of prebiotics in sustaining and boosting the population of probiotics in the gut, promoting long-term digestive health.
These fibers are not digestible by human enzymes but are efficiently fermented by gut microbiota. This fermentation process aids in the proliferation of beneficial bacterial strains, which play a critical role in maintaining a balanced gut environment. Among the various types of prebiotic fibers, inulin, fructooligosaccharides (FOS), and galactooligosaccharides (GOS) are the most prominent. These fibers are found in a wide range of foods, making it relatively easy to include them in your diet.
Common sources of prebiotic fibers include foods like bananas, onions, garlic, asparagus, chicory root, and leeks. Each of these foods offers a unique mix of prebiotic fibers that, when consumed, help nourish beneficial bacteria and enhance their activity. For example, bananas are rich in inulin, while garlic and onions are high in FOS. Regular consumption of these foods not only fosters a more diverse and robust microbiome but also supports various aspects of digestive health.
A well-balanced gut microbiome is crucial for numerous bodily functions, including digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune system regulation. By ensuring a steady intake of prebiotics, you can boost the resilience and functionality of your gut ecosystem. The symbiotic relationship between prebiotics and probiotics underscores the importance of integrating prebiotic-rich foods into your daily diet, thereby naturally enhancing digestive health.
Benefits of a Combined Approach
The powerful relationship between probiotics and prebiotics forms the foundation of optimal digestive health. Probiotics are the beneficial bacteria that reside in our gut, essential for maintaining digestive balance. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that serve as nourishment for probiotics, ensuring their growth and activity. When used together, they create a dynamic duo that promotes a well-functioning digestive system.
Combining probiotics and prebiotics is crucial for ensuring a robust population of beneficial bacteria in the gut. This dual approach helps maintain an optimal microbial environment. For instance, when choosing the best probiotic for gut health, adding prebiotics ensures that these beneficial bacteria have the nutrients they need to thrive. This balanced intake leads to specific health benefits that can transform your digestive health.
One of the most immediate benefits is improved digestion. A healthy gut flora aids in more efficient nutrient absorption and helps break down complex food substances. This balance reduces digestive discomforts like bloating, gas, and constipation. Improved digestive health also means a stronger intestinal barrier, reducing the risk of harmful bacteria or toxins entering the bloodstream.
Another significant benefit is enhanced immune function. Probiotics play a critical role in modulating the immune system. By maintaining a balanced gut flora, your body is better equipped to fight off infections and illnesses. Prebiotics, by supporting these beneficial bacteria, indirectly boost immune defenses.
Additionally, a combined intake of probiotics and prebiotics can help reduce inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a precursor to many health issues, including digestive disorders and metabolic conditions. Probiotics help manage inflammation by producing short-chain fatty acids
(SCFAs), while prebiotics ensure a steady supply of fuel for these probiotics, reinforcing their anti-inflammatory effects.
In essence, using both probiotics and prebiotics together presents a natural and effective strategy for enhancing digestive health. The symbiotic relationship they share not only supports the digestive tract but also contributes to overall well-being, highlighting the importance of including both in your dietary regimen.
Incorporating Probiotics into Your Diet
Incorporating probiotics into your diet can be a simple and effective way to boost your digestive health. Probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi are excellent sources of these beneficial bacteria. Here are some practical tips for seamlessly including these foods in your daily routine.
Yogurt is one of the most accessible sources of probiotics. When choosing yogurt, look for labels that indicate “live and active cultures” to ensure you’re getting a good amount of probiotics. Consider adding a serving of yogurt to your breakfast, either on its own or mixed with fruits and granola for a nutritious start to your day.
Kefir, a fermented milk drink, is another versatile option. It can be enjoyed on its own, added to smoothies, or used as a base for salad dressings. Kefir’s tangy flavor complements various dishes, making it easy to incorporate into your meals without much effort. Plus, it’s available in both dairy and non-dairy forms, catering to different dietary preferences.
Fermented vegetables like sauerkraut and kimchi are traditional probiotic foods rich in beneficial bacteria. Sauerkraut can add a crunchy texture to salads or sandwiches, while kimchi pairs well with rice dishes and can serve as a flavorful side dish. Including a small portion of these vegetables in your meals can diversify your probiotic intake and support your gut health.
Variety is key when incorporating probiotics into your diet. Different probiotic strains offer various health benefits, so consuming a range of probiotic-rich foods can provide a more comprehensive boost to your digestive system. Exploring recipes that include these foods can also make your health regimen more enjoyable. For instance, try a kefir-based smoothie bowl for breakfast, a yogurt parfait for a mid-morning snack, and kimchi fried rice for dinner.
By thoughtfully integrating these probiotic sources into your diet, you can naturally support your digestive health while enjoying a variety of flavors and textures. Remember, consistency and variety are essential for maximizing the benefits of probiotics.
Incorporating Prebiotics into Your Diet
Incorporating prebiotics into your daily diet is a strategic way to naturally enhance digestive health. Prebiotics are non-digestible food components that feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut, playing a key role in maintaining a balanced microbiome. Here are practical ways to increase your prebiotic intake.
Start by including foods that are high in prebiotics, such as garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, oats, and chicory root. These foods are versatile and can easily complement a variety of dishes.
For breakfast, try adding sliced bananas and a tablespoon of chia seeds to your oatmeal. Both ingredients are rich in prebiotics, making for a nutritious and gut-friendly start to your day. Alternatively, you can blend a banana with spinach and a handful of oats into your smoothie for an extra prebiotic boost.
Lunch is another opportunity to incorporate prebiotics. A salad with mixed greens, raw onions, and a side of grilled asparagus can be a refreshing and healthful choice. You could also make a homemade hummus dip with garlic and chicory root, providing a prebiotic-rich addition that pairs well with whole grain bread or fresh veggies.
For dinner, roasted vegetables like garlic and onions can be paired with a lean protein source, such as chicken or fish. Additionally, adding prebiotic-rich leeks to soups and stews enhances both the flavor and the digestive benefits of your meal.
It is generally recommended to aim for 5-10 grams of prebiotics daily. By consistently including prebiotic-rich foods in your diet, you can promote a healthier gut microbiome, which in turn can improve overall digestive health and well-being.
Choosing the Right Supplements for Probiotics and Prebiotics
Choosing the right supplements for probiotics and prebiotics can be crucial for enhancing your digestive health. While it’s possible to obtain these beneficial bacteria and dietary fibers through food alone, supplements can provide a more consistent and higher dose, especially for those with specific health needs or dietary restrictions. Opting for high-quality supplements can simplify the process of improving gut health efficiently.
Reasons for Choosing Supplements
There are various situations where supplements might be essential. Individuals with gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome or inflammatory bowel disease, often require a concentrated supply of probiotics to manage their symptoms effectively. Similarly, those with dietary restrictions or poor dietary habits may struggle to consume enough prebiotic fibers naturally. In these cases, supplements ensure that the necessary dose is consistently met.
Selecting High-Quality Supplements
When choosing supplements, it’s important to focus on a few key factors listed on the label. Look for probiotic supplements that contain a variety of bacterial strains, rather than just one or two. Multistrain supplements tend to be more effective. The number of colony-forming units (CFUs) is also crucial; an effective supplement typically contains between 10 billion and 100 billion CFUs. For prebiotic supplements, look for ingredients like inulin, fructooligosaccharides (FOS), and galactooligosaccharides (GOS), which are indicators of quality.
Reputable Brands and Potential Side Effects
Choosing reputable brands is as important as understanding the content of the supplement. Trusted brands usually undergo third-party testing to ensure product purity and potency, which can be verified by certifications from organizations like NSF International or the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP). However, even high-quality supplements can cause mild and temporary side effects, such as bloating or gas. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help minimize discomfort.
Integrating Supplements Safely into Your Routine
To effectively incorporate probiotics and prebiotics into your daily routine, consider taking them at the same time each day for consistency. Probiotic supplements are most effective when taken with a meal that contains some fat, as this enhances their absorption. Prebiotic supplements can typically be mixed with water or juice. As with any new supplement, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to tailor the regimen to your specific health needs.
Monitoring Your Digestive Health and Making Adjustments
Monitoring your digestive health is essential when introducing probiotics and prebiotics into your diet. Being mindful of the changes in your body helps you determine the benefits and effectiveness of these additions. One effective method is to keep a detailed food and symptom diary. Recording what you eat each day, along with any physical changes or symptoms, allows you to identify patterns that can inform your dietary choices. This can include noting improvements in digestive comfort, bowel movement frequency and regularity, bloating, or other gastrointestinal symptoms.
Signs of improved digestive health might include reduced bloating, more regular bowel movements, and a general feeling of digestive comfort. Conversely, persistent or worsening symptoms might indicate the need for adjustments. Symptoms like increased gas, constipation, or diarrhea could suggest that the specific probiotics and prebiotics being used aren’t suitable for your body or that the dosage needs tweaking.
Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance tailored to your unique health needs. These experts can help you choose the best probiotic for gut health, recommend the right strains and dosages, and assist in identifying foods that may work synergistically with your supplements. Healthcare professionals can also help you interpret your food and symptom diary more accurately, offering valuable insights and adjustments to optimize your digestive health.
Ultimately, the goal is to find a balanced approach that promotes a healthy gut flora and overall digestive well-being. Regularly reassessing your dietary choices and making informed adjustments based on careful monitoring and professional advice can greatly enhance the benefits of probiotics and prebiotics, leading to a more balanced and efficient digestive system.